Binomial
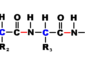
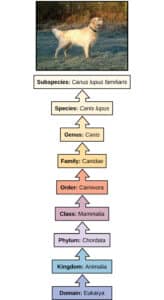
binomial (binomial name) Each organism is named using a Latin-based code consisting of a combination of two names, the first being a generic (genus) name and the second a specific trivial name, which, together,
constitute the scientific name of a species. Lupinus perennis, or wild blue lupine, is an example. Both names are italicized, and both names used together constitute the species name. This is an example of the binomial nomenclature, critical to the system of classification of plants and animals. Linnaeus, a Swedish naturalist, developed the system in the 18 th century. The hierarchy lists the smallest group to largest group: species, genus, family, order, class, division, and kingdom. The first person to formally describe a species is often included, sometimes as an abbreviation, when the species is first mentioned in a research article (e.g., Lupinus perennis L., where L. = Linnaeus, who first produced this binomial name and provided an original description of this plant).