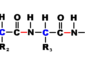
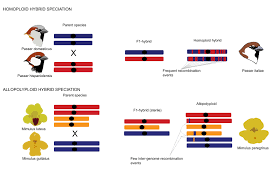
Allopolyploid
allopolyploid A type of polyploid (having a nucleus that contains more than two sets of chromosomes) species, often a plant, resulting from two different species interbreeding and combining their chromosomes. Hybrids are often sterile because they do not have sets of homologous chromosome. Making pairing nonexistent unless two diploid hybrids double the chromosome numbers. Resulting in a fertile allote- traploid that now contains two sets of homologous chromosomes. Plant breeders find that this is beneficial, since it is possible to breed the advantages of different species into one. Triticale (a “new” grain created by crossing rye and durum wheat) is an allopolyploid that was developed from wheat and rye. Some crops are naturally allopolyploid, such as cotton, oats, tall fescue, potatoes, wheat, and tobacco. It is estimated that half of all angiosperms (flowering plants) are polyploid.