Amphipathic molecule
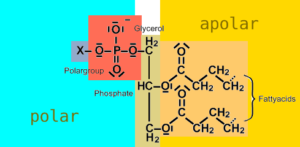
amphipathic molecule A molecule that has both a hydrophilic (water soluble, polar) region and a hydrophobic (water hating, nonpolar) region. The hydrophilic part is called the head, while the hydrophobic part is called the tail. Lipids (phospholipids, cholesterol and other sterols, glycolipids [lipids with sugars attached], and sphingolipids) are examples of amphi- pathic molecules.
Amphipathic molecules act as surfactants, materials that can reduce the surface tension of a liquid at low concentrations, and are used in wetting agents, demisters, foaming agents, and emulsifiers.