Angiosperm
angiosperm A flowering plant. There are close to 250,000 species of flowering plants, second in abundance only to insects. All have three basic organs (roots, stems, and leaves) and represent the most abundant and advanced terrestrial plants. Generally include trees, herbaceous plants, herbs, shrubs, all grasses, and some aquatic plants. Angiosperms are the source of most of the food on which human beings and other mammals rely. Many raw materials and natural products that provide the infrastructure for modern civilizations.
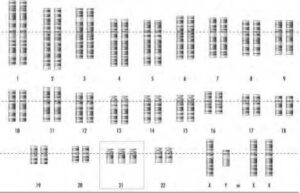
| An example of aneuploidy for an individual possessing three copies of a particular chromosome instead of the normal two copies. (Courtesy of Darryl Leja, NHGRI, National Institutes of Health) |
Angiosperms are divided into two large groups. The dicotyledonea, or dicotyledons (also called magno- liopsida). The larger of the two groups, includes trees and shrubs and herbaceous plants. Dicots have two seed leaves (cotyledons) in the embryo. While The smaller of the two groups is the monocotyledoneae, or monocotyledons (also called liliopsida). And that include rice, corn, palms, bananas, coconuts, grasses, lilies, orchids, and garden plants. Monocots have a single seed leaf in the embryo.
The life cycles of the angiosperms have several advantages over those of conifers, or gymnosperms. The only other group of seed-bearing plants, and from which scientists believe the angiosperms evolved during the Cretaceous era some 145 million years ago. They reproduce via flowers instead of cones. Their ovules are embedded in female sporophylls. Instead of being exposed on a bare ground surface (e.g., apple). the gametophyte is reduced. And seeds are enclosed in fruits that develop from the ovary or related structures.
Angiosperms Flower:
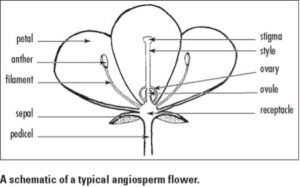
Angiosperms have a true flower. And that is either a highly modified shoot with modified stem and leaves. Or a condensed and reduced compound strobilus (conelike structure) or inflorescence (flower cluster). Floral parts are in the form of sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels. in the same fashion the ovules—the structure that develops in the plant ovary and contains the female gametophyte—are contained within the megasporophylls that are sealed in most angiosperm families. Pollination is facilitated by wind, water, or many animals. Self-pollination as well as parthenogenesis. A process by which embryonic development is initiated directly from an unfertilized cell are common. Double fertilization occurs in all members of the phylum to produce the unusual stored food tissue called endosperm. Sexual reproduction in flowering plants occurs by this process of double fertilization in which one fertilization event forms an
embryo, and a second fertilization event produces endosperm, a polyploid embryo-nourishing tissue found only in the angiosperms. Seeds are dispersed through a variety of forms such as fruits, follicles, capsules, berries, drupes, samaras, nuts, and achenes. Angiosperm is a combination of the Latin word angi- (enclosed) and the Greek word sperma (seed)