Acid precipitation
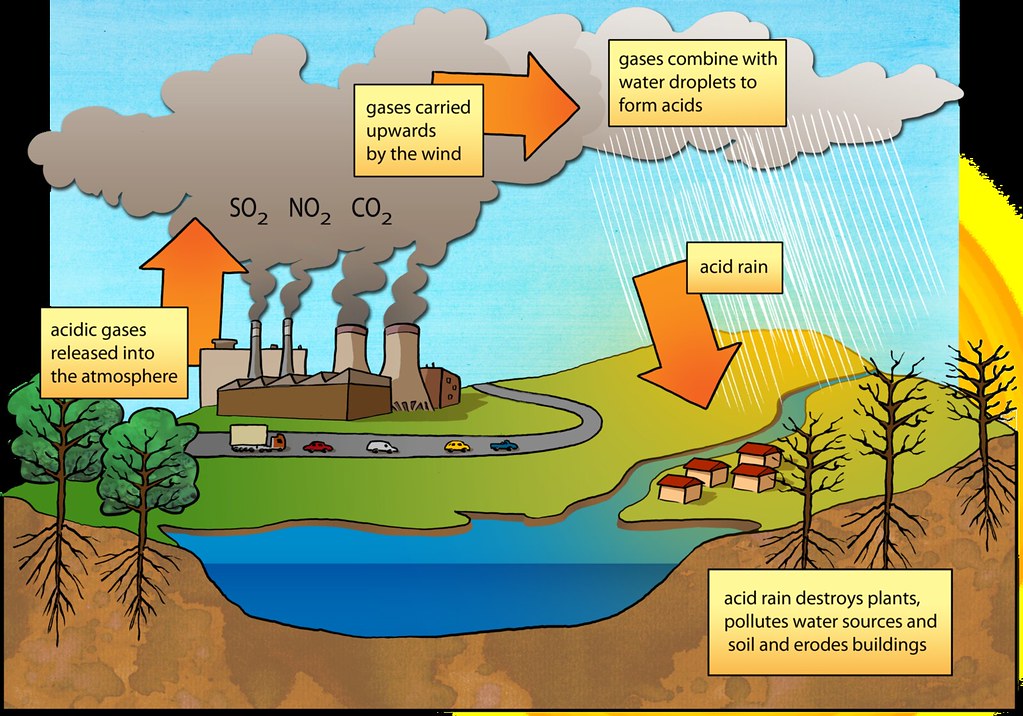
Acid precipitation is the term used to describe precipitation with a pH less than 5.6 since pure precipitation—e.g., rain—is somewhat acidic (result of the reaction between water droplets and carbon dioxide, producing carbonic acid).
Among this include rain, fog, snow, and dry deposition. Reacting with water vapor, anthropogenic (man-made) pollutants like carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, ozone, nitrogen and sulfur oxides, and hydrocarbons create it. Mostly from burning coal and other fossil fuels, these contaminants are connected to the weathering (eating away) of marble buildings and the acidification of freshwater lakes ( consequentially killing fish), sulfur dioxide—which combines easily with water vapor and droplets—i.e., has a short residence period in the atmosphere—has been connected to Natural processes in the biosphere can also result in this phenomenon.