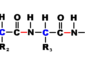
Acid
A chemical capable of donating a hydron (proton, H+) or capable of forming a covalent bond with an electron pair. It increases the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution, and it can react with certain metals, such as zinc, to form hydrogen gas. A strong acid is a relatively good conductor of electricity. Examples of strong acids are hydrochloric (muriatic), nitric, sulfuric, while examples of mild acids are sulfurous and acetic (vinegar). The strength of an acidic solution is usually measured in terms of its pH (a logarithmic function of the H+ ion concentration). Strong acid solutions have low pHs (typically around 0-3), while weak acid solutions have pHs in the range 3-6.