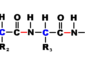
Androgens Steroid
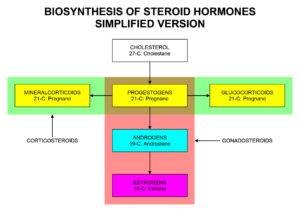
androgens Steroid sex hormones, such as testosterone secreted by the testes in males. Also others secreted by the adrenal cortex in humans and higher animals, as well as by the adrenal glands and ovaries in mammals. Androgens stimulate the development and maintenance of the male reproductive system such as sperm production, sexual behavior, and muscle development. Secondary sex characteristics such as the growth of pubic hair in females is also a product of androgens, as is the deepening of the voice at puberty.
Testosterone is present in a number of forms. Such as free testosterone, as testosterone bound to a protein, sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG), and as dihydrotestosterone. Testosterone and synthetic androgens (anabolic steroids) have been used for infertility, athletic enhancement, erectile dysfunction, and libido problems. But their use can cause side effects such as muscle weakness, muscle atrophy, little facial and body hair, and even changes in the size of the genitalia. Prolonged use can damage the liver, and their use is banned in many sports.
Other androgens are androsterone (excreted in urine), which reinforces masculine characteristics; dihydrotestosterone. Which is a metabolite synthesized mainly in the liver from free testosterone by the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase. And which levels are proportionally correlated to sex drive as well as erectile capabilities; and dehydroepiandrosterone. These are adrenal androgens that have been linked to puberty and aging.