Aneuploidy
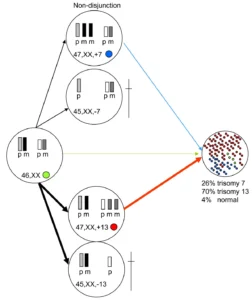
aneuploidy Aneuploidy is the gain or loss of individual chromosomes from the normal diploid set of 46. And it is the most common cytogenetic abnormality caused when homologous chromosomes fail to separate during the first division of meiosis.
When a loss of a chromosome occurs, it is called monosomy and is rarely seen in live births. Since most monosomic embryos and fetuses are lost to spontaneous abortion at very early stages of pregnancy. one exception to this is the loss of an X chromosome. Which produces Turner syndrome in about one out of every 5,000 female births.
The more common gain of a single chromosome is called trisomy. And has been associated with various cancers. A common autosomal trisomy is Down’s syndrome in humans.
Another form of aneuploidy is called nullisomy. It is the loss of both pairs of homologous chromosomes and is almost always fatal to humans. Since humans have no extra disposable chromosomes in the genome.
Tetrasomy is the gain of an extra pair of homologous chromosomes and is a rare chromosomal aberration. it can cause metopic craniosynostosis, facial anomalies, cranial asymmetry, atrioseptal defects, hydronephrosis, flexion contractures of the lower limbs, sensorineural hearing loss, and mental retardation.