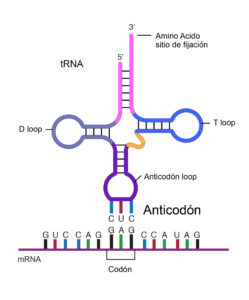
Anticodon
anticodon A specialized sequence of three nucleotides on a tRNA (transfer ribonucleic acid) molecule. The anticodon associates with a complementary triplet of bases—the codon—on an mRNA (messenger RNA) molecule during protein synthesis.
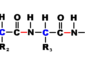
The tRNA molecule acts like a “ferry” whose job is to “pick up a passenger” (read the code from the mRNA) and then “shuttle it” (dock to the corresponding amino acid) into place. The other end of the tRNA molecule has an acceptor site where the tRNA’s specific amino acid will bind.
The 20 amino acids in the table below can create 64 different tRNA molecules, 61 for tRNA coding and three codes for chain termination (pairing up with “stop codons” that end the mRNA message), and each amino acid can create more than one set of codons.
| A = Adeninez | |
| C = Cytosine | |
| G = Guanine | |
| U = Uracil | |
| Alanine | GCC, GCA, GCG, GCU |
| Arginine | AGA, AGG, CGU, CGA, CGC, CGG |
| Asparagine | AAC, AAU |
| Aspartic Acid | GAC, GAU |
| Cysteine | UGC, UGU |
| Glutamic Acid | GAA, GAG |
| Glutamine | CAA, CAG |
| Glycine | GGA, GGC, GGG, GGU |
| Histidine | CAC, CAU |
| Isoleucine | AUA, AUC, AUU |
| Leucine | UUA, UUG, CUA, CUC, CUG, CUU |
| Lycine | AAA, AAG |
| Methionine (initiation) | AUG |
| Phenylalanine | UUC, UUU |
| Proline | CCA, CCC, CCG, CCU |
| Serine | UCA, UCC, UCG, UCU, AGC, AGU |
| Threonine | ACA, ACC, ACG, ACU |
| Tryptophan | UGG |
| Tyrosine | UAC, UAU |
| Valine | GUA, GUC, GUG, GUU |
| “Stop” | UAA, UAG, UGA |