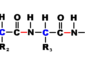
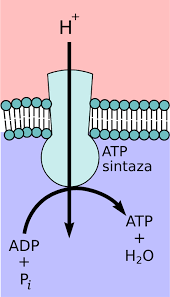
ATP synthase
ATP synthase (proton translocating ATPase):
ATP synthase, A protein complex (a chemiosmotic enzyme) that synthesizes adenosine triphosphate (ATP) from adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and enables phosphate coupling with an electrochemical ion gradient across the membrane. It is found in cellular membranes and the inner membrane of mitochondria. The thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts, and the plasma membrane of prokaryotes. The protein consists of two portions. A soluble fraction that contains three catalytic sites and a membrane-bound portion that contains anion channels. it functions in chemiosmosis, the use of ion gradients across membranes, with adjacent electron transport chains, and it uses the energy stored across the photosynthetic membrane (a hydrogen-ion concentration gradient) to add inorganic phosphate to ADP, thereby creating ATP. This allows hydrogen ions (H+) to diffuse into the mitochondrion.
atrioventricular valve A valve in the heart between each atrium and ventricle. It prevents a backflow of blood when the ventricles contract.